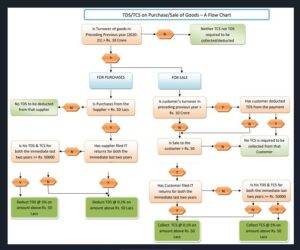
In this manual, you’ll discover the fundamentals of Indian payroll taxes and statutory compliances, including why it’s important, how to execute it, what a good payroll process looks like, and more. Let’s begin!
Payroll refers to a full process that starts with the employee punching in and ends with the creation of his or her payslip, not only the payment of salary to employees. Working on a month-to-month basis will be a laborious procedure that needs devoted resources. Nevertheless, a reliable payroll system can easily manage all of your salary-related tasks.
Payroll computation by hand is not a simple task for any organization. It takes a lot of effort and time. A payroll solution is really important in this situation. Having a payroll system that is scalable and reliable is essential in a large country like India with its diverse state-level laws and geography.
Payroll: What Is It in India?
Payroll is the act of paying employees by an organization. It also refers to the total sum of money that the firm pays its workers. It entails, as a corporate function,
- creating organizational policies for things like compensation, flexible benefits, and leave encashment.
- Define the basic, variable, LTA, and HRA pay components on a payslip.
- other payroll components, such as stipends for meals,
- The actual calculation of gross salary, statutory as well as non-statutory deductions, and arriving at the net pay
- revealing employee compensation
- filing returns and remitting payments such as TDS, PF, and other dues to the proper authorities
In India, how is payroll determined?
The payroll process comprises calculating the employees’ due pay, often known as their “net pay,” which is the amount left over after deducting all necessary taxes and other expenses.
The formula used to determine net pay is as follows:
Net pay = Gross Income – Gross Deduction, and
Where,
Gross Income or salary = All types of regular income + allowances + any one-time payment or benefit.
Gross Deduction = All types of regular deductions + statutory deductions + any one-time deductions.
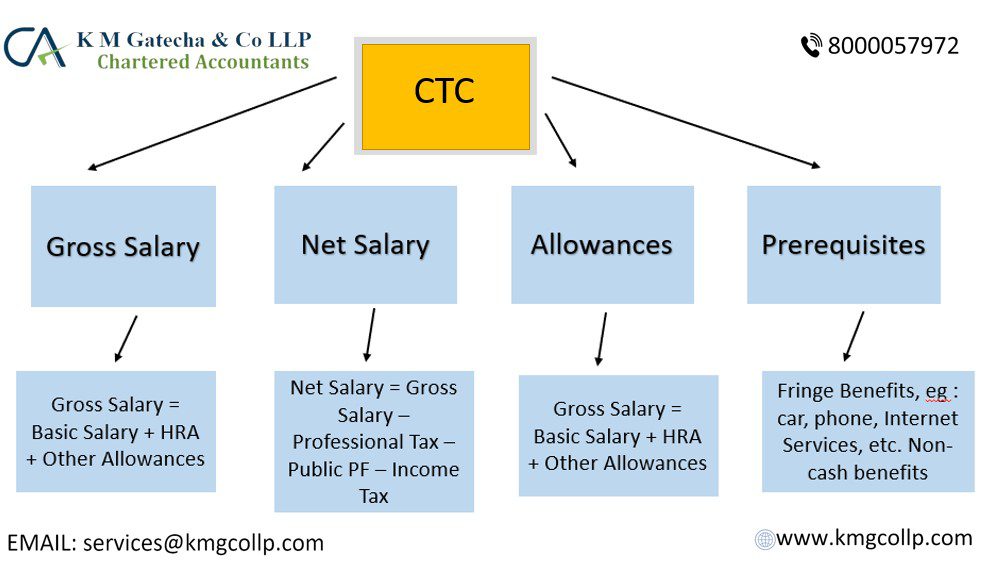
What Components Make Up the Indian Salary Structure?
Every payroll in India includes a monthly salary and wages distribution that is made up of a number of essential parts that work together to form a salary package. Both employers and employees need these components in order to calculate taxes, PF, ESI, benefits, LTA, etc.
Indian payroll taxes and statutory compliances
Businesses must make sure that the payroll in India complies with all applicable laws and rules.
Having to deal with legal problems related to regulatory compliances is a big worry for businesses. Because of the growing risks of non-compliance, it is essential for businesses to follow Indian HR laws.
What Are Statutory Rule & laws, In India?
Regarding statutory compliance, there are a number of regular legal obligations that businesses should adhere to when managing their payroll in India. India’s labour rules for private businesses are same throughout and do not vary depending on the company.
Specific sectors are subject to different HR compliance rules:
LABOR LAWS IN INDIA
Social Security
- The Employee Provident Fund Act, 1952
- The Labor Welfare Fund Act, 1965
- The Employee’s State Insurance Act, 1948
- The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
- The Personal Injuries (Compensation Insurance) Act, 1963
- The Weekly Holidays Act, 1942
- The Workmen’s Compensation Act, 1923
- The Children (Pledging of Labour) Act 1938
Wages
- The Payment of Wages Act, 1936
- The Minimum Wages Act, 1948
- The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
- The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
Industrial Relations
- The Industrial Dispute Act, 1946
- The Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946
- Shops and Establishment Act
- The Trade Union Act, 1926
- The Factories Act, 1948
- The Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946.
Benefits for Women
- The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
- The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act, 2013
Frequently Asked Questions: –
What are employee payroll taxes?
A payroll tax is a tax paid on the wages and salaries of employees to finance social insurance programs like Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance.
What is statutory compliance in payroll?
Statutory compliance refers to the legal framework put in place by the central or state government to regulate business operations. In this case, it’s the framework surrounding payroll.
What’s the Difference Between Payroll and Income Taxes?
The key difference is that payroll taxes are paid by employer and employee; income taxes are only paid by employers. However, both payroll and income taxes are required to be withheld by employers when they make payroll.
The federal government levies payroll taxes on wages and self-employment income and uses the revenue to fund Social Security, Medicare, and other social insurance programs. Payroll taxes have become an increasingly important part of the federal budget over time, as the chart below shows.
Disclaimer: The main goal of this article is to “assist investors in making informed financial decisions.” The above information is provided only for educational purposes. Readers are advised to exercise caution and seek professional counsel before relying on the above information. K M Gatecha & CO LLP is not liable for any loss or harm incurred by readers who take action based on the information provided in this article. “Please keep in mind that the opinions expressed in this Blog/Comments Section/Forum are clarifications intended for the readers’ reference and guidance as they investigate further on the topics/questions raised and make informed decisions. These are not intended to be investment advice or legal advice.”