Introduction
India has the second-largest internet user base in the world. India’s e-commerce market after “India Goes Digital” has the fastest-growing country in the world. The rapid popularity and acceptance of e-commerce across the world have changed the whole economy of the country. In this article, we have discussed all about ‘business compliance requirements for e-commerce business in India’. With common people having easy access to the internet, E-commerce offered the easiest and most convenient mode of executing business operations with the added benefit of being time-saving. Moreover, the Government incentives provided to E-Commerce players have contributed to the sprouting up of a number of e-commerce players in a short span of two to three years. For instance, as per the recent FDI policies, e-commerce marketplaces can get 100% Foreign Direct Investment under the Automatic Route. With the Model GST Law in the pipeline, the government is trying to streamline the process of tax collection and avoid the menace of double taxation, which affects the E-commerce players the most, etc.
The Digital India, Start-up India, Make in India, and Skill India initiative by the Government seeks to promote the growth of e-commerce presence in India.
What is E-Commerce Business:
E-commerce means buying and selling of goods and services including digital products over a digital and electronic network. Chapter XI B of Model GST Law contemplates Electronic Commerce to mean:
- supply or receipt of goods and/or services, or
- Transmitting of funds or data, over an electronic network, primarily the internet,
- by using any of the applications that rely on the internet, like but not limited to e-mail, instant messaging, shopping carts, web services, etc. irrespective of the fact whether the payment is conducted online and whether or not the ultimate delivery of the goods and/or services is done by the operator.
Models of E-Commerce Business
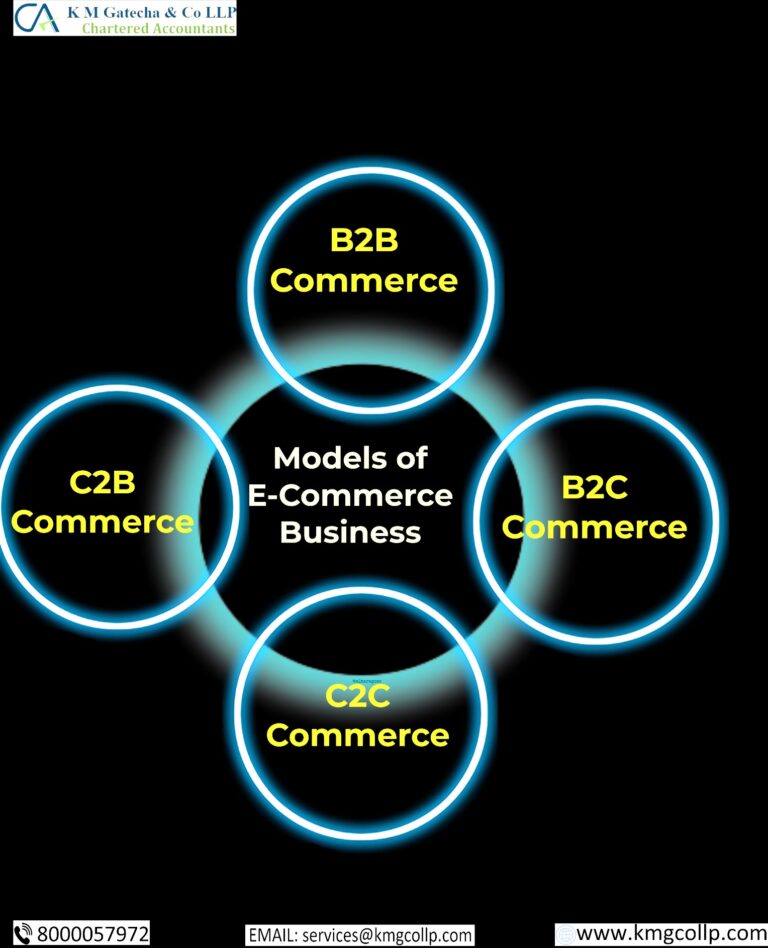
If you are starting an e-commerce business, odds are you will fall into at least one of these four general categories. Each has its benefits and challenges, and many companies operate in several of these categories simultaneously.
- B2B – Business to business
In a B2B business model, a business sells its product or service to another business. Sometimes the buyer is the end-user, but often the buyer resells to the consumer.
2. B2C – Business to consumer
In the B2C model, a consumer goes to the website, selects a catalog, orders the catalog, and an email is sent to the business organization.
3. C2B – Consumer to business
This is the reverse of B2C, it is a consumer-to-business. So, the consumer provides a good or some service to the Company.
4. C2C – Consumer to consumer
Consumer-to-consumer e-commerce or C2C is simply business between private individuals or consumers. Consumer to consumer, where the consumers are in direct contact with each other. No company is involved. It helps people sell their personal goods and assets directly to an interested party. example eBay, Olx, Quikr.
Legal Compliances for E-Commerce Business in India
For a successful establishment of an E-commerce business, it is required to fulfill the following compliances:
Company Incorporation or LLP:
When Entrepreneurs start their new business or e-commerce, there is common confusion about which form of business will be best for them. Which will benefit them more. A Private Limited Company is one of the most common types of business form in India. In India, Limited Liability Partnerships are new in comparison to Private Limited Companies.
GST registration is mandatory:
For the successful estabilization of an e-commerce business, GST registration is mandatory. According to a recent notification by the Central Board of Indirect tax and Customs, any business with a turnover of 40 lakhs and above must register for goods and services (GST).
Payment Gateway:
A payment gateway is a technology used by merchants to accept debit or credit card purchases from customers. The term includes not only the physical card-reading devices found in brick-and-mortar retail stores but also the payment processing portals found in online stores.
Opening of Bank Account:
Opening a bank account in the name of the Company or LLP plays a key role in growing your business. It provides financial solutions that include, instant refund, bulk payment, real-time reconciliation, instant settlement of funds, real-time collection, and deposit payments under your company name.
Legal Documents:
Drafting and Execution of various Legal agreements & contracts such as Website Term User Agreement, Employment Agreement, etc.; Memorandum of Association, Articles of Association, Website Privacy Policy, and other related documents.
Cyber Law Due Diligence:
The need for cyber security is growing as the business is growing and using more and more space in the digital world. it is one most the most important aspect of a due diligence process to conduct thorough due diligence in the area of cyber security.
Data protection & Appointment of NODAL officer:
According to a notification issued by the consumer affairs ministry. Under the new rule, e-commerce companies would have to appoint a nodal (Network-oriented Document Abstraction Language) officer to ensure compliance. E-commerce entities must comply with the Information Technology (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal data.
Frequently Asked Questions
Opening a bank account in the name of the Company or LLP plays a key role in growing your business. It provides financial solutions that include, instant refund, bulk payment, real-time reconciliation, instant settlement of funds, real-time collection, and deposit payments under your company name.
Each company shall nominate a Nodal Officer, who shall either be a Director or Chief Financial Officer, or Company Secretary of the company. A company may appoint one or more Officers as Deputy Nodal officers (maximum up to 5) to assist the Nodal Officer for the purposes of verification of claim.
Table of Contents
Toggle


