How to claim exemptions from Long Term Capital Gains
Long Term Capital Gains are defined as profits on sale of assets (movable or immovable) which have been held for:
- 3 years or 36 months (or more) in case of movable assets. Movable assets include:
- Jewelry,
- Debt-oriented mutual funds.
- 2 years or 24 months (and more) in case of immovable assets such as:
- House,
- Building (commercial),
- And all other types of real estate (except for inherited property).
- 1 year or 12 months (and more) in case of short-term assets such as:
- Listed shares,
- Equity oriented mutual funds etc.
 ,chartered accountant,audit firm in Ahmedabad,gst consultant,tax consultant,tax advisor,statutory audit,internal audit,stock audit,concurrent audit,itr filing,gst filing,tds filing,
,chartered accountant,audit firm in Ahmedabad,gst consultant,tax consultant,tax advisor,statutory audit,internal audit,stock audit,concurrent audit,itr filing,gst filing,tds filing,
What is not considered as a capital asset?
The following are not considered as capital assets for the purpose of Long-Term Capital Gains:
- Stock, consumables, or raw materials held for business purpose,
- Clothes or furniture bought for personal use,
- Rural agricultural land,
- Special bearer bonds which were issued in 1991,
- Gold bonds issued by the Central Government,
- Gold deposit bonds,
- The deposit certificates issued under Gold Monetization Scheme (2015).
Now that we have understood what is considered a capital asset and what is the period for the qualification of long-term capital gain, we should know what the exemptions are allowed in case of capital gains.
These are the exemptions that are allocated by the Government of India for the taxpayers to avail of:
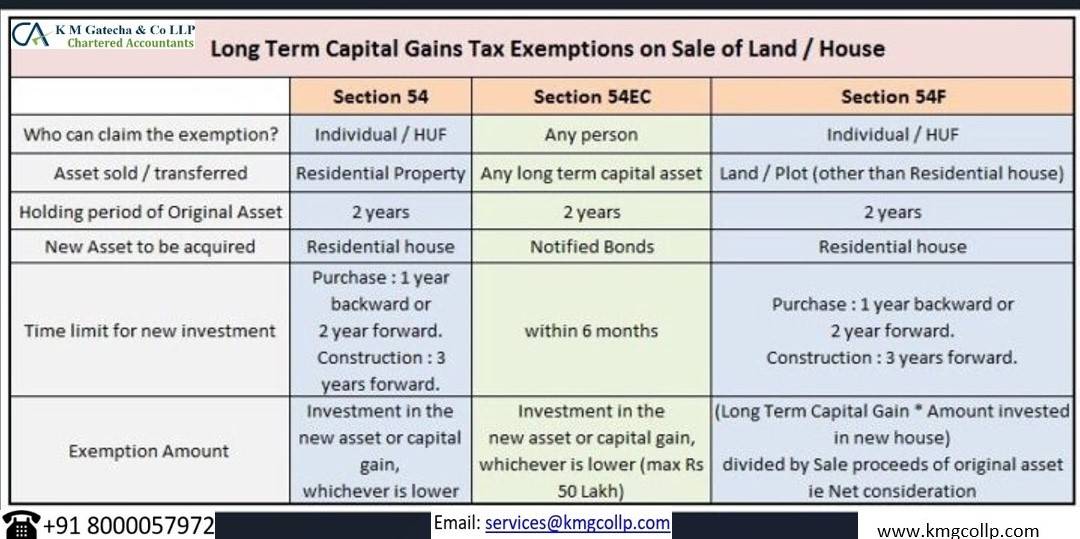
- Under Section 54:
- If the capital gains earned are from selling a residential property, then the capital gains can be exempted by buying up to 2 other residential properties. This, however, is only allowed if the following conditions are met:
- The properties must be purchased within 2 years of sale or 1 year from transfer of ownership,
- In case of under construction property, the property should be completed within 3 years of transfer of ownership of sold property,
- Newly acquired property should not be sold within 3 years of purchase,
- The purchased property must be in India.
- Under Section 54F:
- If long term capital gains are acquired from sale of assets other than residential property then the capital gains that are re-invested in buying property within 2 years of selling assets (3 years in case of under-construction property), are exempt from Long Term Capital Gain Tax.
- The exemption stands invalid if the purchased property is sold within 3 years of purchase.
- Under Section 54EC:
- The upper limit of re-investment is INR 50 lakhs under section 54EC,
- If the capital gains are re-invested in specific bonds notified by the Government of India, then the capital gains that are re-invested, are exempt from taxation.
- These re-invested bonds cannot be sold within 5 years of purchase or investment.
- The investment must be made within 6 months of sale of assets otherwise the exemption is not applicable.
- Under Capital Gains Accounts Scheme:
- This scheme is a deferment of LTCG tax rather than an exemption.
- If any individual is not able or not looking to re-invest the capital gains within the above given conditions, then he/she can deposit the gains in this account and can re-invest it in property within 3 years for construction of house or 2 years for purchasing new house.
- The above deposit must be done before filing of Income Tax Return of the Financial year in which sale has been done.
- If the capital gains earned are from selling a residential property, then the capital gains can be exempted by buying up to 2 other residential properties. This, however, is only allowed if the following conditions are met:
Frequently asked questions on how to claim exemptions from Long Term Capital Gains
Capital Gain is defined as any profit acquired from sale of capital assets.
- The tax rate on LTCG is 20% tax and 3% cess on total amount of profit/gain.
A resident of India (individual or HUF) can avail of the exemptions. The exemptions do not apply for companies or Nonresidents
The above exemption can be only claimed under both if the capital gains arise from sale of residential property and the gains are partly re-invested under both sections. The sections 54 and 54F are mutually exclusive and cannot be availed of together.
Yes, an Individual can re-invest for an amount more than the capital gain but in Section 54EC the upper limit of re-investment stands at INR 50 lakhs.
Table of Contents
Toggle