- Gratuity Exemption -10(10d) Under Income Tax: The act provides for the payment of gratuity to workers employed in every factory, mine, oil field, plantation, port, railways, shop & Establishments or educational institution employing 10 or more persons on any day of the proceeding 12 months.
Gratuity Exemption -10(10d) Under Income Tax: Gratuity is a benefit for retirement. Tip Act, 1972 demonstration conceives in giving retirement advantage to the laborer who have delivered long and unsullied support of the business. A tip is a token of appreciation for long and deserving service. In the past, an employee’s retirement or resignation did not necessitate a reward from the employer.
However, the government enacted the Payment of Gratuity Act in 1972, making gratuity payments mandatory for all employers with more than ten employees.A shop or establishment to which the Act has become applicable shall continue to be governed by the Act even if the numbers of persons employed falls below 10 at any subsequent stage.
Here employees are defined as those hired on the company’s payroll. Trainees and interns are not eligible for this compensation. 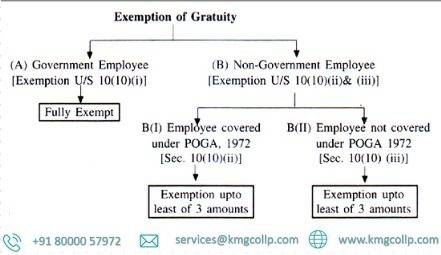
Eligibility criteria forGratuity Exemption -10(10d) Under Income Tax
Gratuity shall be payable to an “employee” on the termination of his employment after he has rendered continuous service for not less than five years.
- On his superannuation.
- On his retirement or resignation.
- On his death or disablement due to accident or disease.
Note:However, the condition of five years of continuous service is not necessary if service is terminated due to death or disablement.
To whom is Gratuity exemption- 10(10d) under income tax Payable? Gratuity is normally payable to the employee himself, however in the case of death of the employee it shall be paid to his nominee & nomination has been made to his heirs. In case the nominee is a minor; share of the minor shall be deposited with the controlling authority who shall invest the same for benefit of the minor, until he/she attains majority.
Maximum amount payable under the Gratuity exemption- 10(10d) under income tax
Gratuity payable to government employees is fully exempt.For non government employee covered under Payment Of Gratuity Act,1972, the maximum limit for exemption is Rs 20 lakhs and for any other employees, the maximum limit of exemption is Rs 10 Lakhs. [Section 4(3)] [Of course, employer can pay more. Employee has also right to get more if obtainable under an award or contract with employer, as made clear in section 4(5)].
Nomination facility: – Yes, by filling Form “F” at the time of new joinee formality, each employee is required to nominate one or more member of his family, as defined in the Act, who will receive the gratuity in the event of the death of the employee.
Forfeiture of Gratuity Exemption -10(10d) Under Income Tax:- The gratuity of an employee whose service have been terminated for any Act of willful omission or negligence causing any damage or loss to or destruction of property belonging to the employer, gratuity shall be forfeited to the extent of the damage or loss caused. The right of forfeiture is limited to the extent of damage. The gratuity payable to an employee shall be wholly forfeited:
- If the services of such employee have been terminated for his riotous or disorderly conduct or any other act of violence on his part, or
- If the service of such employee have been terminated for any act which constitutes an offense involving moral turpitude, provided that such offense is committed by him in the course of his employment.
Applicability to contract Employee:- Yes, the only criterion is to serve at least 5 years of service at a stretch.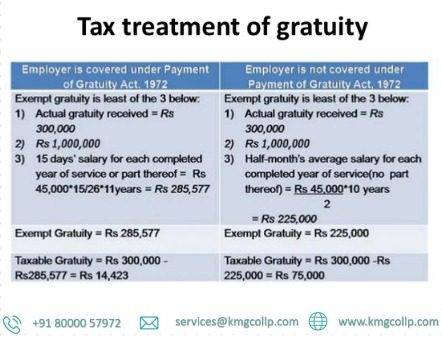
Calculating Gratuity exemption- 10(10d) under income tax
- a) In regard of Representatives covered Under the Installment of Tip Act, 1972:
The Act states that the amount of the gratuity is equal to 15 days’ pay divided by the number of years worked by you. In this context, wage means the basic salary plus the dearness allowance. At the time of your resignation or retirement, take the last month’s salary (basic plus dearness allowance). This is divided by 26. You get your daily pay from this. Add 15 days to this number, and then add the number of years of service you have provided.
Assuming you have placed in 10 years and seven months in an association, your administration period will be taken to be 11 years. However, the duration of your service will only be considered to be 10 years for the purposes of this calculation if it exceeds 10 years and 5 months.
Consider an example. Assume that your typical month to month pay is Rs 26,000. 1,000 rupees per day will be paid to you. Divide this number by 15, then by 10. After ten years of service, you are eligible for a gratuity of Rs 1.5 lakh.
For example: The following formula will be used to determine the amount of gratuity: Gratuity is equal to the salary that was drawn the most recently divided by 15/26 and the number. of long periods of administration
Your last drawn compensation will involve your essential + DA. Your service time will be rounded up to the nearest full year when calculating your Gratuity exemption- 10(10d) under income tax.
- b) Employees who are not covered by the 1972 Payment of Gratuity exemption- 10(10d) under income tax:
The method of calculating gratuity exemption is different for employees who are not employed by the government and are not subject to this Act. The average salary is first determined: This is done by taking the average of the last ten months’ salary (which includes the basic, dearness, and commission as a percentage of the employee’s turnover). ignoring fractions, divide this average salary by 30.
Presently, duplicate this sum by 15 and further with the quantity of long periods of administration put in. Those who are not covered by the Gratuity Act are disadvantageed by dividing the daily salary by 30 instead of 26.
For example: Tip will be determined according to the underneath recipe Tip = Last drawn compensation x ½ x No. of service years Your final salary will include your basic pay plus DA and a commission on sales based on turnover. Your service period will not be rounded up to the nearest full year when calculating your gratuity. Any fraction of a year will be ignored when calculating completed years.
For example, on the off chance that the representative has a complete help of 20 years, 10 months and 25 days, just 20 years will be figured into the computation.
Tax treatment of gratuity :- For the purpose of exemption of gratuity under sec.10 (10) the employees are divided under three categories:
- Any death cum retirement gratuity received by Central and State Govt. employees, Defense employees and employees in Local authority shall be exempt.
- Any gratuity received by persons covered under the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972shall be exempt subject to following limits:-
For every completed year of service or part thereof, gratuity shall be paid at the rate of fifteen days wages based on the rate of wages last drawn by the concerned employee.
The amount of gratuity as calculated above shall not exceed Rs. 20,00,000/- (Limit increased to Rs. 20 Lakh with effect from 29.03.2018, earlier limit was Rs. 10 Lakh.)
- In case of any other employee, gratuity received shall be exempt, subject to the following exemptions
Exemption shall be limited to half month salary (based on last 10 months average) for each completed year of service or Rs. 10 Lakhs whichever is less.
Where the gratuity was received in any one or more earlier previous years also and any exemption was allowed for the same, then the exemption to be allowed during the year gets reduced to the extent of exemption already allowed, the overall limit being Rs. 10 Lakhs.
As per Board’s letter F.No. 194/6/73-IT(A-1) Dated 19.06.73 exemption in respect of gratuity is permissible even in cases of termination of employment due to resignation. The taxable portion of gratuity will qualify for relief u/s 89(1).
Gratuity payment to a widow or other legal heirs of any employee who dies in active service shall be exempt from income tax subject to provisions mentioned above Circular No. 573 dated 21.08.90). The ceiling of Rs. 20/10 lakh applies to the aggregate of gratuity received from one or more employers in the same or different years.
Taxable under what head:- Gratuity received by an employee on his retirement is taxable under the head “Salary” and gratuity received by the legal heir is taxable under the head” Income from Other Sources”.
FAQs of income tax treatment and eligibility of gratuity act 1972
The exemption based on the increased limit will not apply to the reader’s situation as it only applies to retirements occurring after the raised limit. However, as a government pensioner, whether from the Central or State sector, there is no cap on the amount of gratuity received. The reader’s gratuity is completely exempt under Section 10(10)(i) of the Income Tax Act, regardless of their retirement date, notification, or the nature of their government service. The maximum gratuity amount for government retirees was increased to Rs. 20 lakhs as of January 1, 2016, as part of the Seventh Pay Recommendations to address inflation. It’s important to note that this maximum amount applies to gratuities, but Central or State pensioners can receive gratuities tax-free.
Taxation of gratuity differs for govern-ment and non-government employees. Gratuity received by government emplo-yees is fully exempt from tax. For private sector employees covered under Payment of Gratuity Act, exempted gratuity is computed in the manner specified in the Act.
Groww provides you with a free gratuity calculator which you can use and calculate how much your organization owes you. All gratuity payments are controlled by the laws laid down under the Payment of Gratuity Act 1972. The amount depends on the last drawn salary and the years of service served to the company.
Owner of this information can be reached at K M GATECHA & CO LLP.
Important note: This does not lead to legal advice or legal opinion and is personal view and for information purpose only. It is prepared on the basis of facts available and applicable law.It is suggested to go through applicable provisions of law,latest regulations,judicial announcements, circulars, notifications and clarifications etc before taking any action based on above content.You agree here by that for any action taken on basis of above information in any manner writer or K M GATECHA & CO LLP is not responsible or liable for any omission,reliability,accuracy,completeness,errors or authenticity.This work by professional is just for knowledge purpose and does not constitute any kind of solicitation of work or advertisement.
-
 Section 10 Of Income Tax Act_ Exemptions, Allowances & How To Claim It15/08/2024/0 Comments
Section 10 Of Income Tax Act_ Exemptions, Allowances & How To Claim It15/08/2024/0 Comments -
 Steps to register private limited company15/08/2024/
Steps to register private limited company15/08/2024/ -
 Cancellation of registration under GST26/05/2024/
Cancellation of registration under GST26/05/2024/ -

-
 Introduction to Transfer Pricing in India13/04/2024/
Introduction to Transfer Pricing in India13/04/2024/ -
-

-
 Tax Liability of a NRI24/12/2023/
Tax Liability of a NRI24/12/2023/ -
 Everything about SFT18/12/2023/
Everything about SFT18/12/2023/ -
 Documents to be maintained by NGo or trust17/12/2023/
Documents to be maintained by NGo or trust17/12/2023/ -

-

-
-
-
 Taxation of Charitable/Religious Trust04/09/2023/
Taxation of Charitable/Religious Trust04/09/2023/ -

-
 Application for Filing Clarification – GST09/06/2023/
Application for Filing Clarification – GST09/06/2023/ -
 How to check GST application status09/06/2023/
How to check GST application status09/06/2023/ -

-
 Gift tax under section 56(2)x03/06/2023/
Gift tax under section 56(2)x03/06/2023/ -

-

-

-

-

-
 All about Appeal under GST20/05/2023/
All about Appeal under GST20/05/2023/ -
 Old vs New income tax regime18/05/2023/
Old vs New income tax regime18/05/2023/ -
 All about GSTR 10, GST Amnesty16/05/2023/
All about GSTR 10, GST Amnesty16/05/2023/ -

-
-
 TDS on purchase of goods u/s 194Q17/01/2022/
TDS on purchase of goods u/s 194Q17/01/2022/ -
 Situations of GST refund and process10/01/2022/
Situations of GST refund and process10/01/2022/ -
 Tax on property sale in India05/01/2022/
Tax on property sale in India05/01/2022/ -
 House Rent Deduction in Income Tax01/01/2022/
House Rent Deduction in Income Tax01/01/2022/ -

-

-

Table of Contents
Toggle



